Amazon Redshift Database Developer Guide - Sharing data across clusters in Amazon Redshift
2023年03月30日
Create view.
Shows the output of a regular view that is supported with data sharing. (regular view)
Show the output of a late-binding view that is supported with data sharing. (late-binding view)
Create late-binding view.
Show the output of a materialized view that is supported with data sharing. (materialized view)
Create materialized view.
You can maintain common tables across all tenants in a producer cluster. You can also share subsets of data filtered by dimension columns, such as
The following query returns the account ID in which the current Amazon Redshift cluster resides. You can run this query if you are connected to Amazon Redshift.
The following query returns the namespace of the current Amazon Redshift cluster. You can run this query if you are connected to the database.
Managing permissions for datashares in Amazon Redshift
Creates a datashare
再创建一个Redshift作为consumer.
Creating databases from datashares
To start querying data in the datashare, create a database from a datashare. You can create only one database from a specified datashare.
1. Open the Amazon Redshift console.
2. On the navigation menu, choose Clusters, then choose your cluster. The cluster details page appears.
3. Choose Datashares. The datashare list appears.
4. In the Datashares from other namespaces and AWS accounts section, choose a datashare that you want to create databases from, then click Create database from datashare. The Create database from datashare page appears.
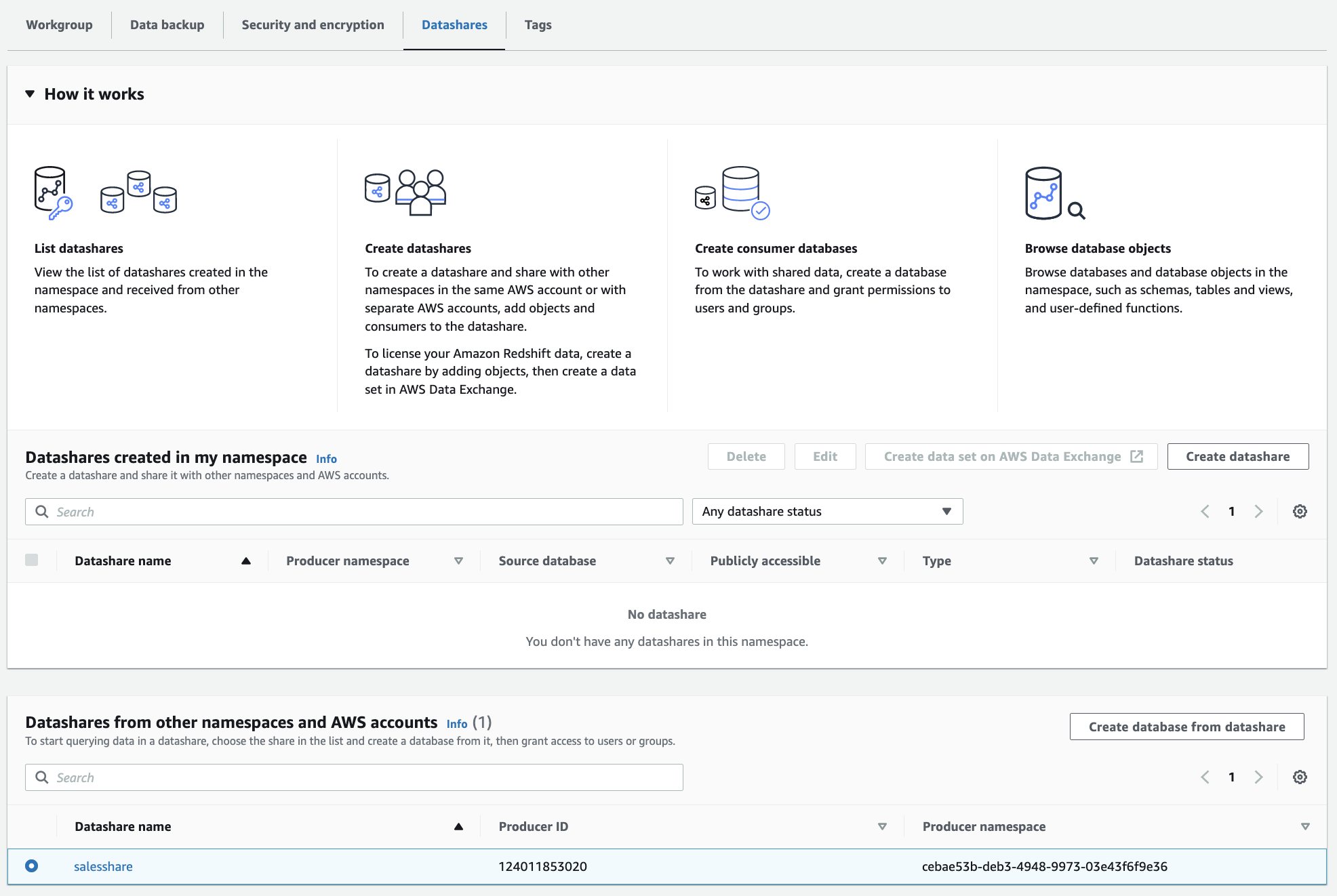
5. In the Database name, specify a database name. 这里,Database name使用“sales_db”。The database name must be 1–64 alphanumeric characters (lowercase only) and it can't be a reserved word.
6. Choose Create.
After the database is created, you can query data in the database.
查看它的namespace的ID。
Grant permissions to access a shared table at the database level and schema level.
On the consumer side, a consumer cluster administrator can determine which users and groups should get access to the shared data. An administrator can control access at the database or schema level. To control access at the schema level, the administrator must create an external schema from the Amazon Redshift database created from the datashare.
The following example grants permissions to access a shared table at the database level and schema level.
References
-
Sharing data across clusters in Amazon Redshift
3-part notation (consumer_database_name.schema_name.table_name
How data sharing works in Amazon Redshift
Working with views in Amazon Redshift data sharing
| View name | Can this view be added to a datashare? | Can a consumer create this view on datashare objects across clusters? |
|---|---|---|
| Regular view | Yes | No |
| Late-binding view | Yes | Yes |
| Materialized view | Yes | Yes, but only with a complete refresh |
create table event( eventid integer not null distkey, venueid smallint not null, catid smallint not null, dateid smallint not null sortkey, eventname varchar(200), starttime timestamp); create table category( catid smallint not null distkey sortkey, catgroup varchar(10), catname varchar(10), catdesc varchar(50)); create table sales( salesid integer not null, listid integer not null distkey, sellerid integer not null, buyerid integer not null, eventid integer not null, dateid smallint not null sortkey, qtysold smallint not null, pricepaid decimal(8,2), commission decimal(8,2), saletime timestamp);
copy event from 's3://skycone-lab-us-west-2/tickit/allevents_pipe.txt' credentials 'aws_iam_role=arn:aws:iam::<111122223333>:role/myRedshiftRole' delimiter '|' timeformat 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SS' region 'us-west-2'; copy category from 's3://skycone-lab-us-west-2/tickit/category_pipe.txt' credentials 'aws_iam_role=arn:aws:iam::<111122223333>:role/myRedshiftRole' delimiter '|' region 'us-west-2'; copy sales from 's3://skycone-lab-us-west-2/tickit/sales_tab.txt' credentials 'aws_iam_role=arn:aws:iam::<111122223333>:role/myRedshiftRole' delimiter '\t' timeformat 'MM/DD/YYYY HH:MI:SS' region 'us-west-2';
Create view.
create view myevent_regular_vw as select eventid, eventname from event; create or replace view myevent_regular_vw as select eventid, eventname from event where eventname = 'LeAnn Rimes';
Shows the output of a regular view that is supported with data sharing. (regular view)
SELECT * FROM dev.public.myevent_regular_vw ORDER BY eventid LIMIT 5;Result:
eventid,eventname 3835,LeAnn Rimes 3967,LeAnn Rimes 4856,LeAnn Rimes 4948,LeAnn Rimes 5131,LeAnn Rimes
Show the output of a late-binding view that is supported with data sharing. (late-binding view)
Create late-binding view.
create view event_lbv as select * from public.event with no schema binding;
SELECT * FROM dev.public.event_lbv ORDER BY eventid LIMIT 5;Result:
eventid,venueid,catid,dateid,eventname,starttime 1,305,8,1851,Gotterdammerung,2008-01-25 14:30:00 2,306,8,2114,Boris Godunov,2008-10-15 20:00:00 3,302,8,1935,Salome,2008-04-19 14:30:00 4,309,8,2090,La Cenerentola (Cinderella),2008-09-21 14:30:00 5,302,8,1982,Il Trovatore,2008-06-05 19:00:00
Show the output of a materialized view that is supported with data sharing. (materialized view)
Create materialized view.
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW tickets_mv AS
select catgroup,
sum(qtysold) as sold
from category c, event e, sales s
where c.catid = e.catid
and e.eventid = s.eventid
group by catgroup;
SELECT * FROM dev.public.tickets_mv;Result:
catgroup | qtysold
----------+---------
Concerts | 195444
Shows | 149905
You can maintain common tables across all tenants in a producer cluster. You can also share subsets of data filtered by dimension columns, such as
tenant_id (account_id or namespace_id), to consumer clusters. To do this, you can define a view on the base table with a filter on these ID columns, for example current_aws_account = tenant_id. On the consumer side, when you query the view, you see only the rows that qualify for your account. To do this, you can use the Amazon Redshift context functions current_aws_account and current_namespace.The following query returns the account ID in which the current Amazon Redshift cluster resides. You can run this query if you are connected to Amazon Redshift.
select current_user, current_aws_account;Result:
current_user,current_aws_account admin,<111122223333>
The following query returns the namespace of the current Amazon Redshift cluster. You can run this query if you are connected to the database.
select current_user, current_namespace;Result:
current_user,current_namespace admin,cebae53b-deb3-4948-9973-03e43f6f9e36
Managing permissions for datashares in Amazon Redshift
Creates a datashare
salesshare and adds a table public.sales to salesshare. It also grants usage permissions on salesshare to a cluster namespace.ERROR: Schema public not part of the datashare salesshare. Please add schema and then add objects under it [ErrorId: 1-64250475-3ae5cea028b4a35e09bc0e7c]如果出现上面的报错,执行SQL:
ALTER DATASHARE salesshare ADD SCHEMA public;
CREATE DATASHARE salesshare; ALTER DATASHARE salesshare ADD TABLE public.sales; GRANT USAGE ON DATASHARE salesshare TO NAMESPACE 'ab23d5cc-82bb-49b3-af42-b02c15e34291';
再创建一个Redshift作为consumer.
Creating databases from datashares
To start querying data in the datashare, create a database from a datashare. You can create only one database from a specified datashare.
1. Open the Amazon Redshift console.
2. On the navigation menu, choose Clusters, then choose your cluster. The cluster details page appears.
3. Choose Datashares. The datashare list appears.
4. In the Datashares from other namespaces and AWS accounts section, choose a datashare that you want to create databases from, then click Create database from datashare. The Create database from datashare page appears.

5. In the Database name, specify a database name. 这里,Database name使用“sales_db”。The database name must be 1–64 alphanumeric characters (lowercase only) and it can't be a reserved word.
6. Choose Create.
After the database is created, you can query data in the database.
查看它的namespace的ID。
Grant permissions to access a shared table at the database level and schema level.
CREATE USER Bob PASSWORD 'sha256|******!'; CREATE GROUP Analyst_group;
On the consumer side, a consumer cluster administrator can determine which users and groups should get access to the shared data. An administrator can control access at the database or schema level. To control access at the schema level, the administrator must create an external schema from the Amazon Redshift database created from the datashare.
The following example grants permissions to access a shared table at the database level and schema level.
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE sales_db TO Bob; CREATE EXTERNAL SCHEMA sales_schema FROM REDSHIFT DATABASE sales_db; GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA sales_schema TO GROUP Analyst_group;
References
-